玉珏图
上一篇
旭日图
下一篇
折线图
Loading...

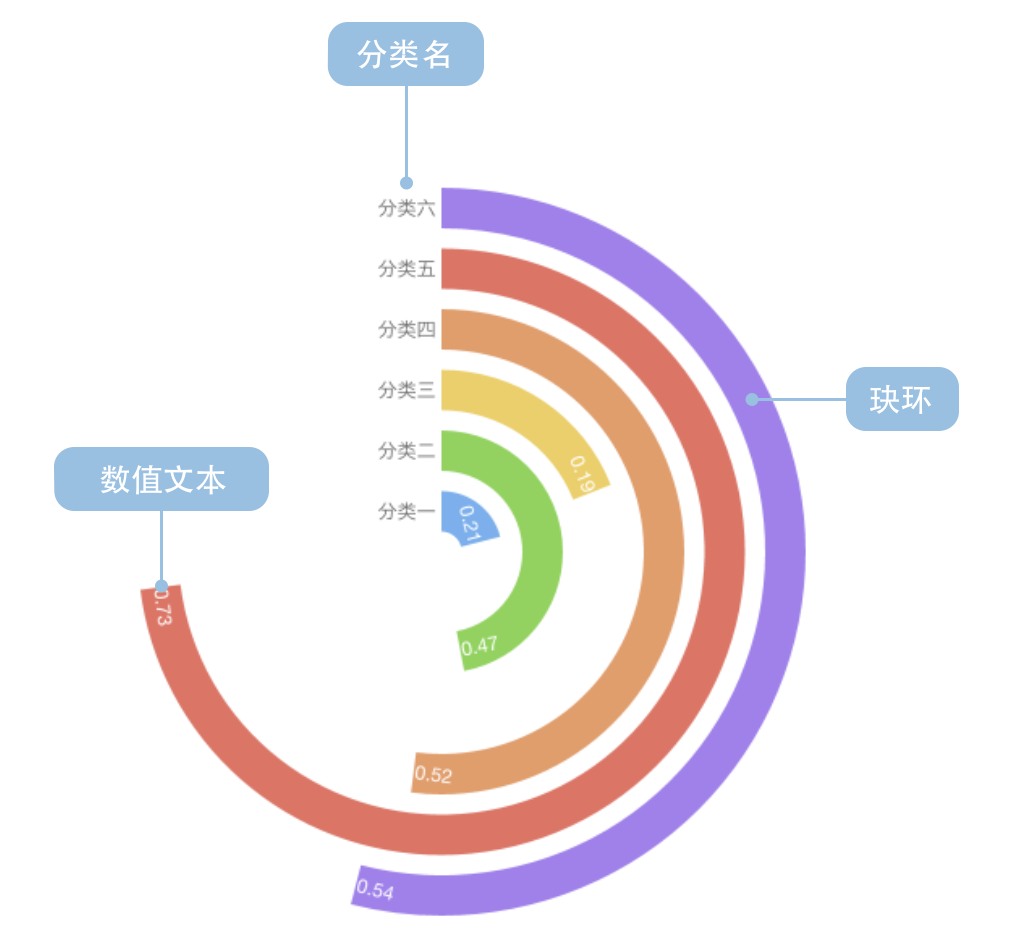
玉珏图(又名环形柱状图),是柱状图关于笛卡尔坐标系转换到极坐标系的仿射变换。其意义和用法与柱状图类似。
玉珏图有半径反馈效应。由于玉珏图中是用角度表示每个珏环数值的大小,角度是决定性因素。所以,哪怕外侧(半径大的)珏环的数值小于内侧(半径小的)珏环,外侧的每个珏环会相对的比里面的珏环更长。这会造成视觉上的误解。
而且因为我们的视觉系统更善于比较直线,所以笛卡尔坐标系更适合于比较各个分类的数值比较。所以玉珏图从实用的角度去看,其更多的是一种审美上的需求。
英文名:Radial Bar Chart
| 图表类型 | 玉珏图 |
|---|---|
| 适合的数据 | 列表:一个分类数据字段、一个连续数据字段 |
| 功能 | 以审美的方式展示分类数据的数值大小对比 |
| 数据与图形的映射 | 分类数据字段映射到环形位置 连续数据字段映射到弧长(角度) 可以用颜色区分不同分类 |
| 适合的数据条数 | 不超过 15 条数据 |
一个完整的玉珏图包含以下构成元素:
例子 1: 展示分类数据的对比(需要排序)
下图反映了美国民众对不同领域中的中美问题关注程度。
| 问题 | 关注人数比例 |
|---|---|
| 台海关系 | 0.21 |
| 中国持续增长的军事力量 | 0.47 |
| 中国对全球环境的影响 | 0.49 |
| 美国对中国的贸易逆差 | 0.52 |
| 中国的人权政策 | 0.53 |
| 来自中国的网络攻击 | 0.54 |
| 中国带走了美国的就业岗位 | 0.60 |
| 中国持有美国巨额国债 | 0.67 |
import { Chart } from '@antv/g2';const chart = new Chart({container: 'container',theme: 'classic',width: 1000,height: 700,});chart.options({type: 'interval',data: [{ question: '台海关系', percent: 0.21, odd: 0 },{ question: '中国持续增长的军事力量', percent: 0.47, odd: 1 },{ question: '中国对全球环境的影响', percent: 0.49, odd: 0 },{ question: '美国对中国的贸易逆差', percent: 0.52, odd: 1 },{ question: '中国的人权政策', percent: 0.53, odd: 0 },{ question: '来自中国的网络攻击', percent: 0.54, odd: 1 },{ question: '中国带走了美国的就业岗位', percent: 0.6, odd: 0 },{ question: '中国持有美国巨额国债', percent: 0.67, odd: 1 },],coordinate: { type: 'radial', innerRadius: 0.2 },encode: {x: 'question',y: 'percent',color: 'odd',},scale: {color: {range: ['rgb(211,0,57)', 'rgb(224,74,116)'],},y: { domain: [0, 1] },},style: {radiusTopLeft: 4,radiusTopRight: 4,},label: {text: 'percent',position: 'inside',style: {fontWeight: 'bold',fill: 'white',},},axis: {x: {label: {autoRotate: true,autoEllipsis: true,style: {fontSize: 10,},},},y: {label: false,grid: false,},},interaction: [{type: 'elementHighlight',background: true,},],});chart.render();
例子 2: 展示各国数据对比
下图反映了各国人民认为气候变化是严重问题的比例。
import { Chart } from '@antv/g2';const chart = new Chart({container: 'container',theme: 'classic',width: 1200,height: 800,});chart.options({type: 'interval',data: [{ country: '中国', percent: 0.18, condition: '特殊' },{ country: '俄罗斯', percent: 0.33, condition: '一般' },{ country: '英国', percent: 0.41, condition: '一般' },{ country: '美国', percent: 0.45, condition: '一般' },{ country: '韩国', percent: 0.48, condition: '一般' },{ country: '加拿大', percent: 0.51, condition: '一般' },{ country: '德国', percent: 0.55, condition: '一般' },{ country: '越南', percent: 0.69, condition: '一般' },{ country: '巴西', percent: 0.86, condition: '一般' },],coordinate: {type: 'radial',innerRadius: 0.3,startAngle: -Math.PI,endAngle: -0.25 * Math.PI,},encode: {x: 'country',y: 'percent',color: 'condition',},scale: {color: {range: ['#2370AE', '#A34265', '#505051'],},},style: {radiusTopLeft: 2,radiusTopRight: 2,},label: {text: 'percent',position: 'inside',style: {fontWeight: 'bold',fill: 'white',fontSize: 10,},},axis: {x: {label: {autoRotate: true,autoEllipsis: true,style: {fontSize: 12,},},},y: {label: false,grid: false,},},interaction: [{type: 'elementHighlight',background: true,},],});chart.render();
例子 1: 未排序的数据会产生误导
简介中提到玉珏图具有半径反馈效应。视觉上半径越大的珏环会看起来更大,半径小的则小。造成玉珏图的误用。所以,我们认为玉珏图使用时必须进行排序。
下面展示错误和正确的对比:
错误示例(未排序):
import { Chart } from '@antv/g2';const chart = new Chart({container: 'container',theme: 'classic',width: 1000,height: 700,});chart.options({type: 'interval',data: [{ country: '巴西', percent: 0.86, condition: '一般' },{ country: '越南', percent: 0.69, condition: '一般' },{ country: '德国', percent: 0.55, condition: '一般' },{ country: '加拿大', percent: 0.51, condition: '一般' },{ country: '韩国', percent: 0.48, condition: '一般' },{ country: '美国', percent: 0.45, condition: '一般' },{ country: '英国', percent: 0.41, condition: '一般' },{ country: '俄罗斯', percent: 0.33, condition: '一般' },{ country: '中国', percent: 0.18, condition: '特殊' },],coordinate: {type: 'radial',innerRadius: 0.2,startAngle: -Math.PI,endAngle: -0.25 * Math.PI,},encode: {x: 'country',y: 'percent',color: 'condition',},scale: {color: {range: ['#2370AE', '#A34265', '#505051'],},},style: {radiusTopLeft: 2,radiusTopRight: 2,},axis: {x: {label: {autoRotate: true,autoEllipsis: true,style: {fontSize: 10,},},},y: {label: false,grid: false,},},interaction: [{type: 'elementHighlight',background: true,},],});chart.render();
在上面的错误示例中,由于数据未排序,外圈的巴西(0.86)会在视觉上显得比内圈的中国(0.18)大很多,但这种视觉差异会被半径效应进一步放大,造成误导。
可以通过颜色或分组来展示多维度的数据对比:
import { Chart } from '@antv/g2';const chart = new Chart({container: 'container',theme: 'classic',width: 1000,height: 700,});chart.options({type: 'interval',data: [{ category: 'A类产品', value: 85, quarter: 'Q1' },{ category: 'B类产品', value: 75, quarter: 'Q1' },{ category: 'C类产品', value: 65, quarter: 'Q1' },{ category: 'D类产品', value: 55, quarter: 'Q1' },{ category: 'E类产品', value: 45, quarter: 'Q1' },],coordinate: { type: 'radial', innerRadius: 0.2 },encode: {x: 'category',y: 'value',color: 'category',},scale: {y: { domain: [0, 100] },},style: {radiusTopLeft: 8,radiusTopRight: 8,},label: {text: 'value',position: 'inside',style: {fontWeight: 'bold',fill: 'white',},},axis: {x: {label: {autoRotate: true,autoEllipsis: true,style: {fontSize: 10,},},},y: {label: false,grid: false,},},interaction: [{type: 'elementHighlight',background: true,},],});chart.render();


