cartesian3D
上一篇
radial
下一篇
helix
Loading...
在 2D 笛卡尔坐标系基础上,通过增加 Z 轴扩展而来。示例
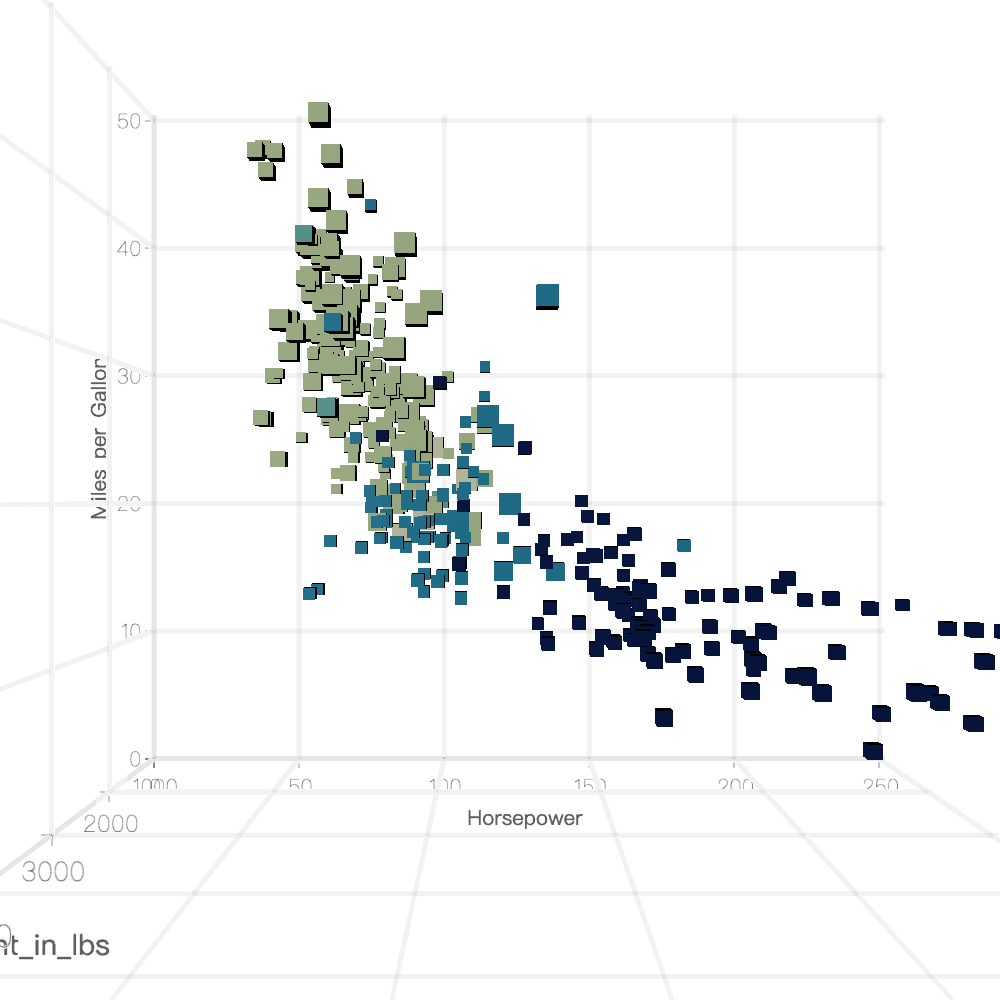
import { Runtime, corelib, extend } from '@antv/g2';import { threedlib } from '@antv/g2-extension-3d';const Chart = extend(Runtime, { ...corelib(), ...threedlib() });const chart = new Chart({container: 'container',renderer,depth: 400,});chart.coordinate({type: 'cartesian3D',});chart.point3D().data({type: 'fetch',value:'https://gw.alipayobjects.com/os/bmw-prod/2c813e2d-2276-40b9-a9af-cf0a0fb7e942.csv',}).encode('x', 'Horsepower').encode('y', 'Miles_per_Gallon').encode('z', 'Weight_in_lbs').encode('size', 'Origin').encode('color', 'Cylinders').encode('shape', 'cube').scale('x', { nice: true }).scale('y', { nice: true }).scale('z', { nice: true }).legend(false).axis('x', { gridLineWidth: 2 }).axis('y', { gridLineWidth: 2, titleBillboardRotation: -Math.PI / 2 }).axis('z', { gridLineWidth: 2 });chart.render();